Complete Guide to Monofilament Yarn Storage Management
2025-03-18
1. Storage environment requirements
2. Storage methods and packaging management
3. Quality control and regular testing
4. Common problems and response strategies
Table of contents
Why storage management is so important
As a high-end textile raw material, the physical properties and chemical stability of PET monofilament yarn play a decisive role in the quality of the final product. Proper storage management can not only extend the life of the yarn and avoid the negative impact of environmental factors on its performance, but also improve production efficiency and reduce loss costs.
Storage environment requirements: the basis of refined management
Temperature control
- Ideal temperature range: It is recommended to maintain the storage temperature between 15℃ and 25℃.
- Too high temperature will accelerate fiber aging and oxidation, and reduce the strength of the yarn.
- Too low temperature may make the fiber brittle and affect processing performance.
- Temperature fluctuation management: Use constant temperature equipment and intelligent temperature control system to ensure that the temperature inside the warehouse is balanced and stable.
Humidity management
- Recommended humidity range: Relative humidity should be maintained at 50% to 65%.
- Too high humidity: It is easy to cause mold growth, yarn adhesion, and even chemical changes.
- Too low humidity: It may cause static electricity problems, causing the yarn to absorb dust or electric shock accidents.
- Humidity control means: Equipped with automatic humidification and dehumidification devices, regularly calibrate humidity sensors, and monitor the warehouse environment in real time.
Lighting and ventilation
- Lighting management:
- Avoid direct sunlight and strong ultraviolet rays, because ultraviolet rays will destroy the molecular structure of fibers.
- Warehouse windows can be designed with blackout cloth or light-isolating glass.
- Ventilation system:
- Maintain good air circulation and use fans and exhaust systems to reduce the concentration of harmful gases.
- Clean ventilation equipment regularly to prevent dust accumulation from polluting yarn.
Storage method and packaging management: Multi-dimensional guarantee of yarn safety
Selection of packaging materials
- Moisture-proof and dust-proof: Select packaging materials with moisture-proof and dust-proof functions, such as anti-static plastic film or special cartons.
- Environmental protection and durability: Give priority to environmentally friendly materials to ensure that the packaging does not age or penetrate during long-term storage.
Storage method design
- Combination of flat and vertical placement:
- Choose the appropriate placement method according to the size, weight and shape of the yarn roll to avoid overlapping and squeezing to cause fiber deformation.
- For large-scale storage, shelf storage can be used, classified display, easy to identify and use.
- Classification storage and label management:
- Classify and store according to the batch, specification, color and production date of the yarn to ensure later traceability and rapid inventory.
- Use clear labels and barcode systems to establish electronic management files.
Automated warehouse management
- Intelligent warehouse system: Use RFID, barcode scanning and warehouse management software to achieve automated tracking and management.
- Data collection and analysis: Regularly collect data such as temperature, humidity, inventory changes, and use big data analysis to optimize storage strategies.
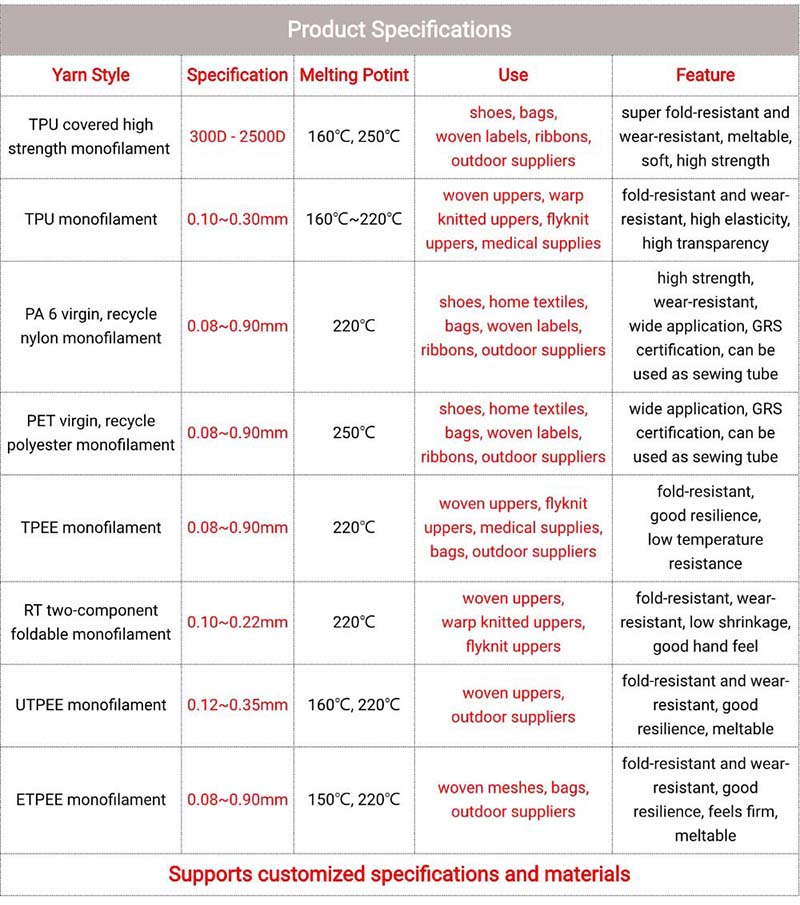
Quality control and regular testing: Ensure that the yarn state is always stable
Regular inspection and monitoring
- Daily inspection:
- A dedicated person will check the warehouse environment and packaging status every day, record the temperature, humidity, ventilation conditions and any abnormal phenomena (such as mildew and insect pests).
- Establish a routine inspection system to ensure that problems can be reported and handled in a timely manner.
- Periodic testing:
- Physical and chemical performance tests are conducted on sample yarns every month or quarter to confirm that no performance degradation occurs during storage.
- Establish detailed quality files to facilitate the traceability and rectification of problematic yarns.
Application of intelligent monitoring equipment
- Environmental monitoring equipment: Install temperature and humidity sensors, smoke alarms and air quality monitors to achieve real-time data collection and alarms.
- Automatic alarm system: Set abnormal thresholds. Once the specified range is exceeded, the alarm system is automatically triggered and the emergency plan is activated.
Common problems and response strategies: Problem prevention and rapid processing
Moisture problem
- Problem manifestation: Yarns are prone to caking and mold after being damp, which affects subsequent processing and product quality.
- Countermeasures:
- Strengthen warehouse moisture-proof facilities, use moisture-proof agents and sealed packaging.
- Check warehouse humidity regularly and adjust environmental parameters when necessary.
Static electricity accumulation
- Problem manifestation: Static electricity accumulates on the surface of yarns in low-humidity environments, which is easy to absorb dust or cause discharge during processing.
- Countermeasures:
- Use anti-static packaging materials and anti-static sprays.
- Humidify the storage area appropriately and install an electrostatic elimination device.
Physical damage and indentation
- Problem manifestation: Improper handling or over-crowding may cause indentation or breakage on the surface of the yarn.
- Countermeasures:
- Establish strict handling and stacking standards and use professional handling tools.
- Optimize warehouse layout to avoid goods squeezing each other and check the stacking situation regularly.
Pests and pollution
- Problem manifestation: During long-term storage, the yarn may be polluted by pests, dust, oil, etc., reducing the use value of the yarn.
- Countermeasures:
- Regularly clean, disinfect and treat the warehouse with insecticides, and use insect repellent packaging.
- Strengthen the management of inbound and outbound storage to prevent external debris from entering the warehouse.

Safety measures and risk prevention: the moat of warehouse management
Fire safety management
- Fire prevention measures:
- Use flame-retardant materials to decorate the warehouse and add fire retardants to the packaging materials.
- Regularly check the circuit system, install fire alarms and automatic fire extinguishing systems to ensure that the risk of fire is minimized.
- Training and drills:
- Regularly organize employees to conduct fire prevention training and emergency drills to improve the safety awareness of all employees.
Anti-theft and monitoring measures
- Security monitoring:
- Equipped with high-precision surveillance cameras and alarm systems to ensure 24-hour monitoring of warehouse entrances and exits.
- Establish a strict entry and exit registration system to prevent unauthorized personnel from entering the warehouse.
- Physical protection:
- Strengthen physical protection measures such as warehouse doors, windows, fences and locks to ensure the safety of goods.
Emergency plans and technical support: key guarantees for preparing for a rainy day
Emergency plan formulation
- Natural disaster response: formulate emergency plans for natural disasters such as earthquakes, floods, and fires, and clarify emergency response measures at all levels.
- Emergency handling: Establish an accident emergency team to preset processing procedures in advance for situations such as warehouse environment out of control and equipment failure.
Technical support and services
- Cooperation with professional testing institutions: Cooperate with third-party testing institutions to conduct regular comprehensive testing and evaluation of storage environment and yarn quality.
- Technical training and update: Regularly invite professionals to conduct technical training for warehouse managers and update the latest storage technology and management concepts.
The storage management of monofilament yarn is a comprehensive project involving environmental control, packaging technology, quality monitoring, safety precautions and emergency response. Through scientific management methods and the continuous introduction of new technologies, enterprises can not only effectively maintain the excellent quality of yarn, but also gain an advantage in the fierce market competition.
 English
English 한국어
한국어 বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার हिन्दी
हिन्दी Türkçe
Türkçe русский
русский




